Dr. Liuh-Yow Chen identified a role of extrachromosomal telomere repeat DNA in ALT cancer development via activating the cGAS-STING DNA sensing pathway
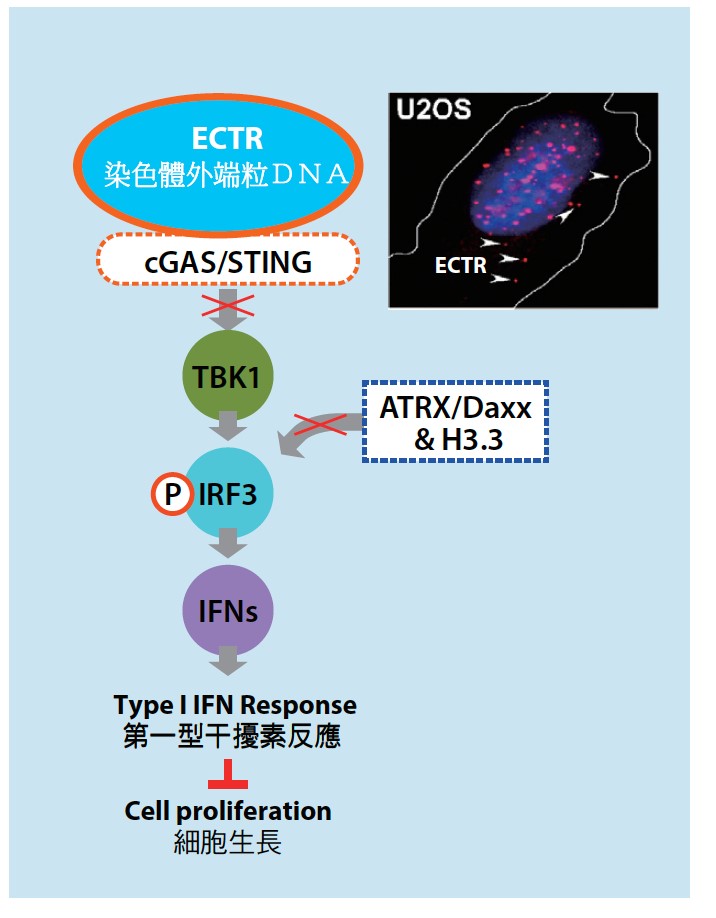
Extrachromosomal telomere repeat (ECTR) DNA is present in cancer cells that maintain telomeres through the alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) pathway. Dr. Liuh-Yow Chen’s lab found that ALT cancer cells are commonly defective in sensing cytosolic DNA due to loss of STING and ATRX/Daxx/H3.3 expressions. This study suggest that the loss of the cGAS-STING pathway may be required to evade ECTR-induced anti-proliferation effects and permit ALT development, and this requirement may be exploited for treatments specific to cancers utilizing the ALT pathway.
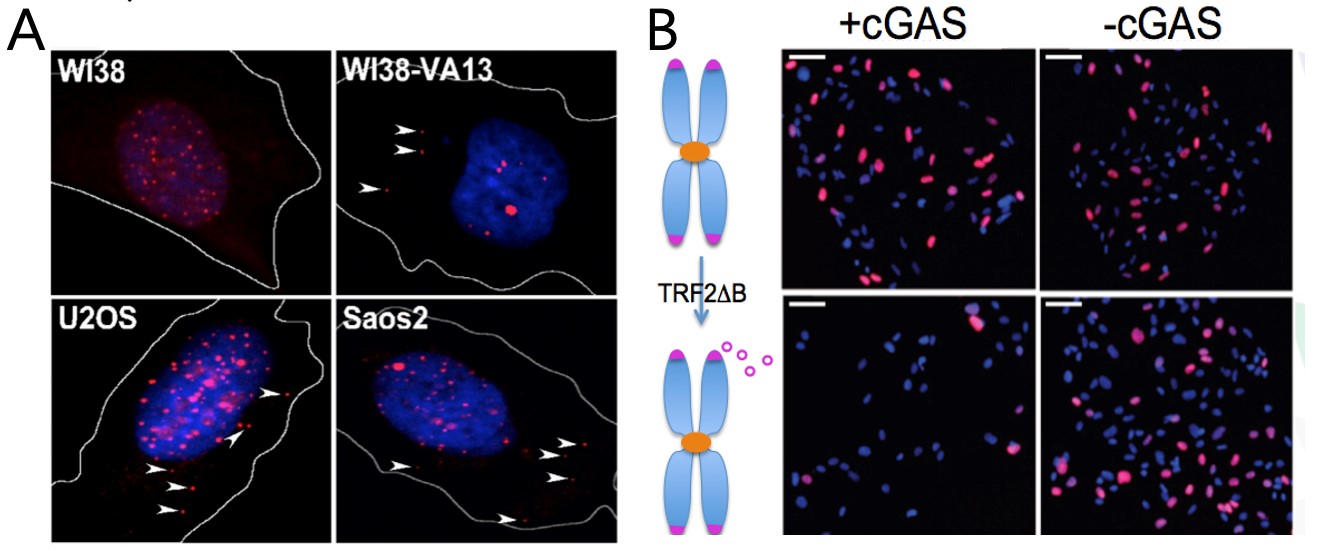
ALT cancer cells contain cytoplasmic ECTR (A). ECTR accumulation impairs proliferation of normal human fibroblasts in a cGAS-dependent manner (B).