Cryo-EM structure of the vaccinia virus entry fusion complex reveals a multicomponent fusion machinery
Dr. Chang, Wen - January, 2026
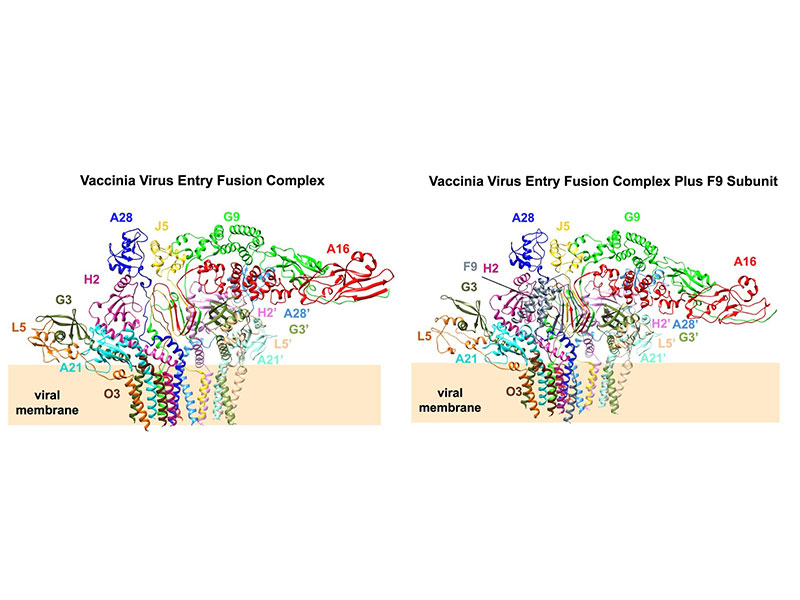
Membrane fusion is essential for viral entry. Unlike class I-III fusion proteins, vaccinia virus (VACV) uses a multicomponent entry fusion complex (EFC). Using cryo–electron microscopy, we determined the full-length structure of the VACV EFC at near-atomic resolution, revealing a 15-protein asymmetric assembly organized into three layers. The central A16/G9/J5 heterotrimer forms the fusion core, stabilized by conserved PXXCW and Delta motifs, and anchors two A28/H2 adaptor dimers linked to peripheral G3/L5/A21/O3 scaffolds. Structural and evolutionary analyses identify a conserved N-terminal domain in A16 containing a myristoyl-binding pocket and a phenylalanine-rich region that stabilizes the trimer and may regulate lipid engagement. An additional component, F9, binds peripherally to J5, A21, and H2 through Delta-like motifs, reinforcing the prefusion architecture. Together, these results define the VACV EFC as a unique multiprotein fusion machinery and provide a structural framework for understanding the mechanism of poxvirus entry and membrane fusion.