Signaling in autism: Relevance to nutrients and sex
Dr. Hsueh, Yi-Ping - January, 2025
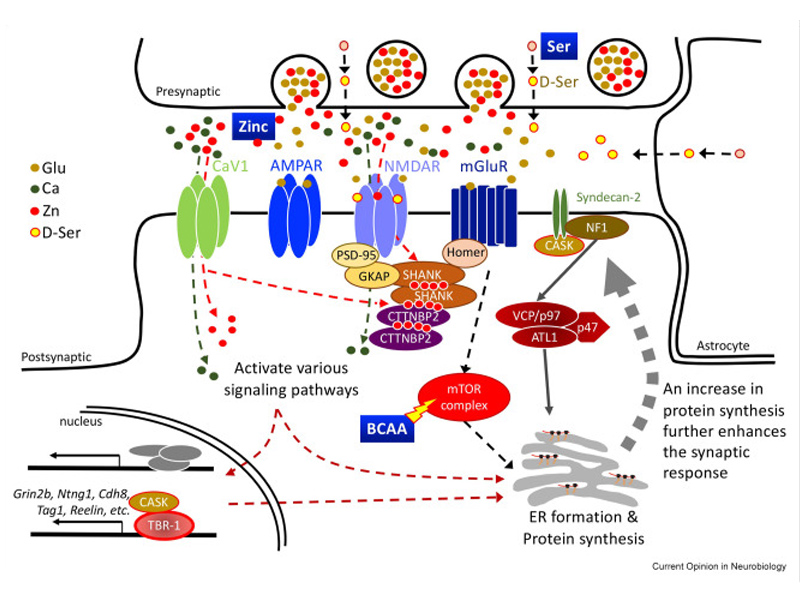
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) are substantially heterogeneous neuropsychiatric conditions with over a thousand associated genetic factors and various environmental influences, such as infection and nutrition. Additionally, males are four times more likely than females to be affected. This heterogeneity underscores the need to uncover common molecular features within ASD. Recent studies have revealed interactions among genetic predispositions, environmental factors, and sex that may be critical to ASD etiology. This review focuses on emerging evidence for the impact of nutrients—particularly zinc and amino acids—on ASD, as demonstrated in mouse models and human studies. These nutrients have been shown to influence synaptic signaling, dendritic spine formation, and behaviors linked to autism. Furthermore, sex-based differences in nutritional requirements, especially for zinc and amino acids, may contribute to the observed male bias in autism, indicating that interactions between nutrients and genetic factors could be integral to understanding and potentially mitigating ASD symptoms.